|
ENERGY DETECTOR |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The SEV/SEC Sunshine Sensor is a versatile solar
radiation sensor.
It uses an array of photodiodes with a unique
computer-generated shading pattern to measure incident solar radiation. |
 |
|
Halmstad
Library, Sweden |
|
A microprocessor calculates the global and
diffuse components of the radiation and determines the sunshine
state.
-
Measures global (total) and diffuse
radiation
-
Measures sunshine duration
-
No moving parts, no shade rings, and
no motorised tracking
-
Outputs 0-10Vdc (SEV) or
4-20mA (SEC)
-
Designed for measuring watt/m2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SEV/SEC |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Datasheet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sunshine Duration
The SEV measures sunshine hours indirectly using a simple
equation based on both the total PAR radiation, and the ratio of
total to direct PAR.
This sunshine algorithm corresponds closely to the World Met
Office threshold of 120 W/m2 in the solar beam for sunshine
duration.
The SEV does not need to be adjusted or repositioned to track the
sun - a distinct advantage over devices with shadow rings.
There are no complex electro-mechanical assemblies and no burnt
paper tracks to interpret. |
 |
|
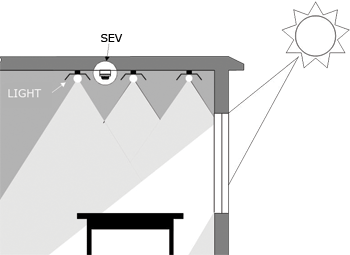
Applications
Solar Blind Control
Modern buildings come with large areas of glass, and
sophisticated building control systems.
The original architectural design inlcuded solar blind controls,
triggered in this instance by the Energy detector included in the
rooftop weather station (not visible in the picture).
Uncomfortable low-angle glare at sunrise and sunset is cut out by
appropriate blind operation on the relevant side of the building.
During the middle of the day, direct sun heat loads on the glass are
reduced by automatic blind closure in the affected area. |